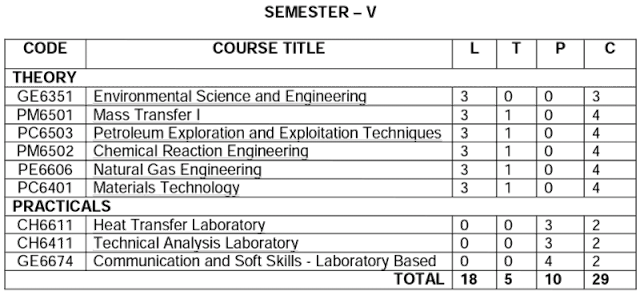
SEMESTER – V
GE6351 Environmental Science and Engineering
PM6501 Mass Transfer I
PC6503 Petroleum Exploration and Exploitation Techniques
PM6502 Chemical Reaction Engineering
PE6606 Natural Gas Engineering
PC6401 Materials Technology
PRACTICALS
CH6611 Heat Transfer Laboratory
CH6411 Technical Analysis Laboratory
GE6674 Communication and Soft Skills - Laboratory Based
GE6351 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
OBJECTIVES: To the study of nature and the facts about environment.
To finding and implementing scientific, technological, economic and political solutions to environmental problems.
To study the interrelationship between living organism and environment.
To appreciate the importance of environment by assessing its impact on the human world; envision the surrounding environment, its functions and its value.
To study the dynamic processes and understand the features of the earth’s interior and surface.
To study the integrated themes and biodiversity, natural resources, pollution control and waste management.
UNIT I ENVIRONMENT, ECOSYSTEMS AND BIODIVERSITY
Definition, scope and importance of Risk and hazards; Chemical hazards, Physical hazards, Biological hazards in the environment – concept of an ecosystem – structure and function of an ecosystem – producers, consumers and decomposers-Oxygen cycle and Nitrogen cycle – energy flow in the ecosystem – ecological succession processes – Introduction, types, characteristic features, structure and function of the (a) forest ecosystem (b) grassland ecosystem (c) desert ecosystem (d) aquatic ecosystems (ponds, streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries) – Introduction to biodiversity definition: genetic, species and ecosystem diversity – biogeographical classification of India – value of biodiversity: consumptive use, productive use, social, ethical, aesthetic and option values – Biodiversity at global, national and local levels – India as a mega-diversity nation – hot-spots of biodiversity – threats to biodiversity: habitat loss, poaching of wildlife, man-wildlife conflicts – endangered and endemic species of India – conservation of biodiversity: In-situ and ex-situ conservation of biodiversity. Field study of common plants, insects, birds Field study of simple ecosystems – pond, river, hill slopes, etc.
UNIT II ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
Definition – causes, effects and control measures of: (a) Air pollution (Atmospheric chemistry- Chemical composition of the atmosphere; Chemical and photochemical reactions in the atmosphere - formation of smog, PAN, acid rain, oxygen and ozone chemistry;- Mitigation procedures- Control of particulate and gaseous emission, Control of SO2, NOX, CO and HC) (b) Water pollution : Physical and chemical properties of terrestrial and marine water and their environmental significance; Water quality parameters – physical, chemical and biological; absorption of heavy metals - Water treatment processes. (c) Soil pollution - soil waste management: causes, effects and control measures of municipal solid wastes – (d) Marine pollution (e) Noise pollution (f) Thermal pollution (g) Nuclear hazards–role of an individual in prevention of pollution – pollution case studies – Field study of local polluted site – Urban / Rural / Industrial / Agricultural.
UNIT III NATURAL RESOURCES
Forest resources: Use and over-exploitation, deforestation, case studies- timber extraction, mining, dams and their effects on forests and tribal people – Water resources: Use and overutilization of surface and ground water, dams-benefits and problems – Mineral resources: Use and exploitation, environmental effects of extracting and using mineral resources, case studies – Food resources: World food problems, changes caused by agriculture and overgrazing, effects of modern agriculture, fertilizer-pesticide problems, water logging, salinity, case studies – Energy resources: Growing energy needs, renewable and non renewable energy sources, use of alternate energy sources. Energy Conversion processes – Biogas – production and uses, anaerobic digestion; case studies – Land resources: Land as a resource, land degradation, man induced landslides, soil erosion and desertification – role of an individual in conservation of natural resources – Equitable use of resources for sustainable lifestyles. Introduction to Environmental Biochemistry: Proteins –Biochemical degradation of pollutants, Bioconversion of pollutants. Field study of local area to document environmental assets – river / forest / grassland / hill / mountain.
UNIT IV SOCIAL ISSUES AND THE ENVIRONMENT
From unsustainable to sustainable development – urban problems related to energy – water conservation, rain water harvesting, watershed management – resettlement and rehabilitation of people; its problems and concerns, case studies – role of non-governmental organization- environmental ethics: Issues and possible solutions – 12 Principles of green chemistry- nuclear accidents and holocaust, case studies. – wasteland reclamation – consumerism and waste products – environment production act – Air act – Water act – Wildlife protection act – Forest conservation act –The Biomedical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules; 1998 and amendments- scheme of labeling of environmentally friendly products (Ecomark). enforcement machinery involved in environmental legislation- central and state pollution control boards- disaster management: floods, earthquake, cyclone and landslides. Public awareness.
UNIT V HUMAN POPULATION AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Population growth, variation among nations – population explosion – family welfare programme – environment and human health – human rights – value education – HIV / AIDS – women and child welfare –Environmental impact analysis (EIA)- -GIS-remote sensing-role of information technology in environment and human health – Case studies.
OUTCOMES: Environmental Pollution or problems cannot be solved by mere laws. Public participation is an important aspect which serves the environmental Protection. One will obtain knowledge on the following after completing the course. Public awareness of environmental is at infant stage. Ignorance and incomplete knowledge has lead to misconceptions Development and improvement in std. of living has lead to serious environmental disasters
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Gilbert M.Masters, ‘Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science’, 2nd edition, Pearson Education (2004).
2. Benny Joseph, ‘Environmental Science and Engineering’, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, (2006).
REFERENCES:
1. R.K. Trivedi, ‘Handbook of Environmental Laws, Rules, Guidelines, Compliances and Standards’, Vol. I and II, Enviro Media.
2. Cunningham, W.P. Cooper, T.H. Gorhani, ‘Environmental Encyclopedia’,Jaico Publ., House, Mumbai, 2001.
3. Dharmendra S. Sengar, ‘Environmental law’, Prentice hall of India PVT LTD,New Delhi, 2007.
4. Rajagopalan, R, ‘Environmental Studies-From Crisis to Cure’, Oxford University Press (2005)
PM6501 MASS TRANSFER I
OBJECTIVE: Students will learn to determine mass transfer rates under laminar and turbulent conditions.
UNIT I DIFFUSION
Diffusion in fluids – Molecular and eddy diffusion – Measurement and calculation of diffusivities – Ordinary diffusion in multi component gaseous mixtures – Diffusion in solids – Molecular and Knudsen diffusion in solids – Theories of mass Transfer –Film theory, penetration theory and surface renewal theories of mass transfer.
UNIT II INTERPHASE MASS TRANSFER
Interphase Mass Transfer – Local and overall mass transfer coefficients – Steady state co current and counter current mass transfer process – Stage and stage efficiencies – Concept of NTU and HTU – Equilibrium and operating lines – JD Factor– Equipments for gas-liquid contact operations – Bubble columns – Tray towers and packed towers.
UNIT III ABSORPTION
Gas Absorption: Principles of absorption and desorption – Selection of solvents for absorption – Tray tower absorber – Absorption factor – Calculation of number of theoretical stages – Murphree efficiency – Point efficiency – Tray efficiency and overall tray efficiency – Calculation of actual number of trays.Packed tower absorber – Tower packing and characteristics – Calculation of NTU, HTU,HETP and height of absorption towers – Absorption with chemical reactions.
UNIT IV DRYING
Drying – Principle and definitions – Estimation of drying rates, drying rate curve – Critical and equilibrium moisture content – Calculation of drying time under constant drying conditions – Different types of dryers.
UNIT V HUMIDIFICATION AND CRYSTALLIZATION
Humidification – Definitions, psychometric charts – Wet bulb temperature – Methods of humidification – Types of cooling towers, spray chambers and spray ponds.Crystallization – Factors governing nucleation and crystal growth – Theory of Crystallization – Classification of crystallizer and their applications – Product size distribution.
OUTCOME: Students apply the mass transfer concepts in the design of humidification columns, dryers and crystallisers.
TEXTBOOKS:
1. McCabe,W.L., Smith, J.C. and Harriot,P., “Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering”, 6th Edition, McGraw – Hill Book Co., 2001.
2. Treybal, R.E., “Mass Transfer Operations”, 3rd Edition, McGraw – Hill Book Co.,1980.
REFERENCES:
1. Coulson, J.M. and Richardson, J.F., “Chemical Engineering”, Vol.I, II and III,Pergamon Press, 1977.
2. Bennett, C.O. and Myers, J.E., “Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer”, McGraw Hill Book Company, 3rd Edition, 1983.
3. Christie J. Geankoplis, “Transport Processes and Unit Operations”, 3rd Edition,Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, 2000.
4. Binay K.Dutta,”Principles of Mass Transfer and Seperation Processes”,PHI Learning Ltd,2013.
PC6503 PETROLEUM EXPLORATION AND EXPLOITATION TECHNIQUES
OBJECTIVE: To understand the stages of oil and gas exploration and production
UNIT I ORIGIN AND OCCURRENCE OF PETROLEUM AND SEDIMENTRARY ENVIRONMENT
Origin of oil – Important factors that control petroleum occurrence – Migration and accumulation – Source and reservoir rocks – Oil bearing rocks – Continental environment – Transitional environment – Marine environment.
UNIT II EXPLORATION METHODS, WELL PROGNOSIS AND ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
Geological exploration methods – Geophysical exploration methods – Geochemicalmethods prognostication – Classification of drilling locations – Economic analysis – Well programme – Geotechnical order.
UNIT III GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURE AND GEOLOGGING
Various traps – Anticline – Fracturing – Well logging – Geological control – Gas logging– Drilling control important formation evaluation using wireline logging data.
UNIT IV DRILLING FLUIDS AND WORK COMPLETION
Drilling Fluids:Function, composition, and classification – Packer fluid – Casing packs –Solids removal – Completion methods – Various stimulation methods.
UNIT V OFF – SHORE TECHNOLOGY
Seismic technology – Sniffer survey – Drilling technology – Off-share rigs – Primary and secondary enhanced oil recovery techniques and methods – Major well complication andRemedies.
OUTCOME: The student will get exposed to different geological and geophysical methods for exploration and exploitation of oil and gas
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Bhagwan Sahay “Petroleum Exploration and Exploitation Practices” Allied Publishers Ltd., Chennai, 1994.
2. Richard Dawe, “Modern Petroleum Technology”, Vol.I, Upstream, 6th Edition, John and Wiley Sons Ltd, 2000.
REFERENCES:
1. Howard B. Bradley, “Petroleum Engineering Handbook”, Society of Petroleum Engineers,1987.
2. Norman J. Hyne., “Nontechnical Guide to Petroleum Geology, Exploration, Drilling and Production”, 2nd Edition, Pennwell Books, 2001.
3. Shay B., “Wellsite Geological Techniques for Petroleum Exploration” Allied Publishers Ltd., 1991.
PM6502 CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING
OBJECTIVE: To gain knowledge on different types of chemical reactors, the design of chemical reactors under isothermal and non-isothermal conditions
UNIT I NON – IDEAL REACTORS
Residence time distribution function and its measurement – Characteristics of tracer – Mean residence time – Conversion in non-ideal flow reactors.
UNIT II HETROGENEOUS PROCESS AND SOLID CATALYSIS
Rate equation for heterogeneous reactions – Nature of catalysis –Adsorption isothermal and rates of adsorption – Desorption and surface reaction analysis of rate equation – Rate controlling steps.
UNIT III GAS – SOLID CATALYTIC REACTORS
Characteristics of catalyzed reactions – Mechanism of solid catalyzed reactions – Pore diffusion resistance combined with surface kinetics – Performance equations for reactors containing porous catalysts.
UNIT IV GAS – SOLID NON – CATALYTIC REACTORS
Selection of the kinetic model – Progressive – conversion model, shrinking – core model – Shrinking-core model for spherical particles of unchanging size – Shrinking-core model for cylindrical particles of unchanging size.
UNIT V GAS – LIQUID REACTIONS
Various ways of carrying out gas – liquid reactions catalyzed by solids – General rate equation – Resistances in series in the gas – liquid reaction on catalyst surface.
OUTCOME: Students gain knowledge on the selection of the reactor for the reaction and its design.
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Levenspiel, O., “Chemical Reaction Engineering”, 3rd Edition, Wiley Asian Edition, 1990.
2. Smith, J.M., “Chemical Engineering Kinetics”, 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill, 1984.
REFERENCES:
1. Scott Fogler, H., “Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering”, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall of India.2009
2. Gavanhe, K.A., “Chemical Reaction Engineering I”, Nirali Prakashan Publishers, 2007.
3. Dawande, D., “Principles of Reaction Engineering”, 1st Edition, Central Techno Publications, 2001.
PE6606 NATURAL GAS ENGINEERING
OBJECTIVE: The objective of studying this subject is that student will be understanding the basic concept and applications of Natural Gas Engineering.
UNIT I PROPERTIES AND COMPOSITION OF NATURAL GAS
Natural gas origin – Composition of natural gas – Sources of Natural gas –Thermodynamics properties – Compressibility factor and chart for natural gas – Heating value and flammability limit of natural gas.
UNIT II ESTIMATION AND PRODUCTION OF NATURAL GAS
Estimation of gas reserves by volumetric method – Production of natural gas –Pressure decline method – Problems in the production of natural gas – Field separation.
UNIT III GAS FROM CONDENSATE OIL FIELDS
Processing of condensate well fluids – Cycling of gas condensate reservoirs – Sweep patterns – Katy cycling plant.
UNIT IV ACID GAS TREATING OF NATURAL GAS
Acid gas removal: Metal oxide process – Slurry process – Amine process –Carbonate washing process – Methanol based process and other process – Sulphur recovery process.
UNIT V DEHYDRATION OF NATURAL GAS AND NGL RECOVERY
Dehydration: Glycol dehydration – Solid desiccant dehydration. NGL Recovery: Refrigeration process – Lean oil absorption process – Solid bed adsorption and membrane separation process – NGL fractionation.
OUTCOME: Students learn the Natural gas processing, Gas Compression, Gas Gathering and Transport Installation, Operation and trouble shooting of natural gas pipelines.
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Katz and Lee “Hand Book of Natural Gas Engineering” McGraw Hill, 1968.
2. Lyons, W.C., “Standard Handbook of Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering”, Vol.2, Gulf Professional Publishing, Elsevier Inc., 2006.
REFERENCES:
1. Katz, D. L. and Lee, R.L., “Natural Gas Engineering”, McGraw Hill, 1990.
2. Dring, M.M., “The Natural Gas Industry – A Review of World Resources and Industrial Applications”, Butterworth, 1974.
3. Saied Mokhatab, William A. Poe, and James G. Speight, “Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing”, Gulf Professional Publishing, Elsevier Inc., 2006..
PC6401 MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: To provide students with a strong foundation in materials science with emphasis on the fundamental scientific and engineering principles which underlie the knowledge and implementation of material structure, processing, properties, and performance of all classes of materials used in engineering systems.
UNIT I STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
Introduction-classification of materials, selection of materials, properties of materials, x-ray crystallography, Bragg's law, x-ray diffraction, electron diffraction, neutron diffraction, structure of NaCl and diamond, Crystal defects - point, line, surface and volume defects, alloy formation, solid solution types, solidification of castings, structural examination using microscopy.
UNIT II METALLURGICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Phase diagrams - isomorphous, eutectic, eutectoid and peritectic system. Diffusion - Fick 's laws. Mechanical properties - tension test, hardness test - brinnel, vickers, rockwell, micro hardness test - shore scleroscope. Impact test, fracture - grifiths' theory, fracture toughness, embrittlement phenomena. Fatigue and creep. Strengthening mechanisms
UNIT III TYPES OF MATERIALS
Classification of steel, Fe-C phase diagram, heat treatment, TTT curves, ausforming, marforming, annealing types, normalizing, tempering, hardening, effect of alloying elements, tool steels, stainless steel, cast iron - malleable and ductile types and properties. Copper and its alloys - brass, bronze, copper – nickel. Aluminium and its alloys, hardening treatment. Al cladding nickel and its alloys, titanium and its alloys, cermets, welding electric and magnetic materials, nano particles and nano structures.
UNIT IV PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF MATERIALS
Metals, semiconductors, insulators, electron theory, band theory, types of magnetism, domain structures, anisotrophy of materials, and application. Soft and hard magnets. Conductivity of materials, zone refining, crystal growth techniques.
UNIT V NON-METALLIC MATERIALS
Ceramic materials - oxides, silicates. Refractories. Glasses, enamels, abrasives, cement and concrete materials. Polymers – classification, reaction, types, mechanisms, deformation of polymers, mechanical, thermal, electrical and chemical behavior. Rubber, silicones, fluoro carbons, composites -FRP, particulates, and laminates.
OUTCOME: Students will be able to understand various material and its properties and manufacturing methods.
TEXT BOOKS:
1. V.Raghavan, “Materials Science and Engineering : A first course”, V Edition, Prentice Hall of India , 2004.
2. Van Vlack L.H , “Elements of Materials Science and Engineering” (Addision Wesley series in metallurgy and materials engineering), VI Edition, Prentice Hall, 6th Edition, 1989.
REFERENCES:
1. WF.Hosford, “Material Science”, Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 2006.
2. C.Srinivasan, “ Science of Engineering Materials”, John Wiley, New York, 1987.
CH6611 HEAT TRANSFER LABORATORY
OBJECTIVE: Students develop a sound working knowledge on different types of heat transfer equipments.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Performance studies on Cooling Tower
2. Batch drying kinetics using Tray Dryer
3. Heat transfer in Open Pan Evaporator
4. Boiling Heat Transfer
5. Heat Transfer through Packed Bed
6. Heat Transfer in a Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
7. Heat Transfer in a Bare and Finned Tube Heat Exchanger
8. Heat Transfer in a Condenser
9. Heat Transfer in Helical Coils
10. Heat Transfer in Agitated Vessels
OUTCOME: Student should be able to calculate heat transfer by conduction, different types of convection using classical models for these phenomena
LIST OF EQUIPMENT FOR BATCH OF 30 STUDENTS
1. Cooling Tower
2. Tray Dryer
3. Open Pan Evaporator
4. Boiler
5. Packed Bed
6. Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
7. Bare and Finned Tube Heat Exchanger
8. Condenser
9. Helical Coil
10. Agitated Vessel
CH6411 TECHNICAL ANALYSIS LABORATORY
OBJECTIVE: To learn basic principles involved in estimation and characterization of industrially important materials.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
I Soap Analysis
a. Estimation of total fatty acid
b. Estimation of percentage alkali content
II. Oil Analysis
a. Estimation of free acid
b. Determination of Saponification value c. Determination of iodine value
III.Cement Analysis
a.Estimation of Silica content
b.Estimation of mixed oxide content
c.Estimation of calcium oxide content
d.Estimation of calcium oxide by rapid method
IV.Coal Analysis
a.Estimation of Sulphur present in coal
b.Ultimate analysis of coal
c.Proximate analysis of coal
V. Analysis of Bleaching Powder
a.Estimation of available chlorine
VI.Analysis of Glycerol
a.Estimation of purity of glycerol
VII. Analysis of fuels
a. Flash point
b. Fire point
c. Cloud point
d. Pour point
e. Aniline point.
VIII.Determination of the molecular weight of the polymer by viscometry.
IX. Calorimetric measurements
X. Conductivity measurement of an electrolyte solution
XI . pH measurements
OUTCOME: At the end of this practical course, the student would have a thorough understanding on the estimation and analysis of chemical compounds.
LIST OF EQUIPMENT FOR BATCH OF 30 STUDENTS
1. Silica Crucible
2. Heating Mantle
3. Muffle Furnace
4. Hot air oven
5. Desiccator
6. Vacuum pump
7. Condenser
8. Reflux Condenser
9. Pensky martens closed cup apparatus
10. Cleveland open cup apparatus
11. Cloud point apparatus
12. Aniline point apparatus
13. Saybolt Viscometer
14. Redwood viscometer
15. Bomb Calorimeter
16. Junkers gas Calorimeter
17. Conductivity meter
18. pH meter
GE6674 COMMUNICATION AND SOFT SKILLS - LABORATORY BASED 0 0 4 2
OBJECTIVES:
To enable learners to develop their communicative competence.
To facilitate them to hone their soft skills.
To equip them with employability skills to enhance their prospect of placements.
UNIT I LISTENING AND SPEAKING SKILLS
Conversational skills (formal and informal) – group discussion and interview skills – making presentations. Listening to lectures, discussions, talk shows, news programmes, dialogues from TV/radio/Ted talk/Podcast – watching videos on interesting events on Youtube.
UNIT II READING AND WRITING SKILLS
Reading different genres of tests ranging from newspapers to philosophical treatises – reading strategies such as graphic organizers, summarizing and interpretation. Writing job applications – cover letter – resume – emails – letters – memos – reports – blogs – writing for publications.
UNIT III ENGLISH FOR NATIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS AND PLACEMENTS
International English Language Testing System (IELTS) – Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) – Graduate Record Examination (GRE) – Civil Service (Language related) – Verbal ability.
UNIT IV SOFT SKILLS (1)
Motivation – self image – goal setting – managing changes – time management – stress management – leadership traits – team work – career and life planning.
UNITV SOFT SKILLS (2)
Multiple intelligences – emotional intelligence – spiritual quotient (ethics) – intercultural communication – creative and critical thinking – learning styles and strategies.
Teaching Methods:
1. To be totally learner-centric with minimum teacher intervention as the course revolves around practice.
2. Suitable audio/video samples from Podcast/YouTube to be used for illustrative purposes.
3. Portfolio approach for writing to be followed. Learners are to be encouraged to blog, tweet, text and email employing appropriate language.
4. GD/Interview/Role Play/Debate could be conducted off the laboratory (in a regular classroom) but learners are to be exposed to telephonic interview and video conferencing.
5. Learners are to be assigned to read/write/listen/view materials outside the classroom as well for graining proficiency and better participation in the class.
Evaluation: Internal: 20 marks
Record maintenance: Students should write a report on a regular basis on the activities conducted, focusing on the details such as the description of the activity, ideas emerged, learning outcomes and so on. At the end of the semester records can be evaluated out of 20 marks.
External: 80 marks Online Test Interview Presentation Group Discussion - 35 marks - 15 marks - 15 marks - 15 marks
Note on Internal and External Evaluation:
1. Interview – mock interview can be conducted on one-on-one basis.
2. Speaking – example for role play:
a. Marketing engineer convincing a customer to buy his product.
b. Telephonic conversation- fixing an official appointment / placing an order / enquiring and so on.
3. Presentation – should be extempore on simple topics.
4. Discussion – topics of different kinds; general topics, case studies and abstract concept.
OUTCOMES: At the end of the course, learners should be able to Take international examination such as IELTS and TOEFL Make presentations and Participate in Group Discussions. Successfully answer questions in interviews.
REFERENCES:
1. Business English Certificate Materials, Cambridge University Press.
2. Graded Examinations in Spoken English and Spoken English for Work downloadable materials from Trinity College, London.
3. International English Language Testing System Practice Tests, Cambridge University Press.
4. Interactive Multimedia Programs on Managing Time and Stress.
5. Personality Development (CD-ROM), Times Multimedia, Mumbai.
6. Robert M Sherfield and et al. “Developing Soft Skills” 4th edition, New Delhi: Pearson Education, 2009.
Web Sources:
http://www.slideshare.net/rohitjsh/presentation-on-group-discussion
http://www.washington.edu/doit/TeamN/present_tips.html
http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/words/writing-job-applications
http://www.kent.ac.uk/careers/cv/coveringletters.htm
http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newCDV_34.htm